
These sterile areas include the gown front, from chest to the sterile field level, and the sleeves from two inches above the elbow to the cuff. Once the scrubbed person dons the sterile surgical gown, the gown's sterility is limited to the gown portions directly viewed by the scrubbed person. 2,4 These barriers protect the patient from the transmission of microorganisms from the surgical team. In addition to scrub attire, scrubbed persons must wear a sterile surgical gown, mask, and gloves within the sterile field to establish bacterial barriers. All surgical team members wear scrub attire. Sterile members or "scrubbed" personnel work directly in the surgical field while the nonsterile members work in the periphery of the sterile surgical field. The surgical team is made up of sterile and nonsterile members. Scrubbed persons function within a sterile field. The principles of aseptic technique include the following principles.

It is the responsibility of each surgical staff member to understand the meaning of these principles and to incorporate them into their everyday practice. The principles of aseptic technique play a vital role in accomplishing the goal of asepsis in the operating room environment. They should be used by institutions to provide direction and information on perioperative practice as they incorporate them into their own policies and procedures. 3 These guidelines are not to be considered policies. The standards and recommended practices, developed by the Association of periOperative Registered Nurses (AORN), are guidelines to be used by the surgical team to achieve the optimal level of technical and aseptic practice when caring for their patients in the perioperative setting. 1 The surgical team accomplishes this by creating and maintaining the sterile field and by following aseptic principles aimed at preventing microorganisms from contaminating the surgical wound. The goal of asepsis is to prevent the contamination of the open surgical wound by isolating the operative site from the surrounding nonsterile environment. However, operating room activities pertaining to asepsis and aseptic practices have the greatest direct impact upon the surgical team in helping to reduce the patient's risk to surgical site infection. Some of these activities include patient risk assessment, environmental cleaning, disinfection and sterilization of instrumentation, patient antibiotic prophylaxis, and the use of standard precautions. Proper postioning of tubings, etc.Preventing surgical site infection in the operating room is the primary goal of the surgical team, and all activities performed by the team support this goal.

#Infection control and medical asepsis skin#
Maintain itergrity of skin and mucous membrane Between contact with different clients in high- risk units Before and after handling dressings or touching open wounds Before performing invasive procedure like administration of injections, suction, catheterization, etc Before contact with clients who are susceptible to infection This is recommended in the following situations, Protect own clothing from direct contact with infected materials Damp dusting should be done to prevent scattering of dust, etc in the air Use separate thermometer for infectious patients Discourage sharing of bedpans, urinals, basins, eating utensils, etc. Disposable gloves should be worn to prevent direct contact with wastes or infected materials Careful handling of waste like urine, faeces, emesis and blood is important Wearing of masks is important once the nurse herself has infection or deals with clients suffering from Avoid talking directly into the client’s face to prevent droplet infections Empty and dispose of drainage suction bottles according to agency policy Keep drainage tubes and collection bags of the patient s to prevent accumulation of serous fluid under the Bottled solutions should be placed with tight caps as per instructions Keep the patients bedside unit clean, dry and biologically safe Disposal of contaminated needles and syringes in moisture- resistant, puncture-proof container Proper disposal of wastes and contaminated articles Bathing with soap and water to remove secretion, drainage, perspiration, etc Involving the use of heat, radiation, chemical processes, etc, which use various solutions or Sterilization of contaminated objects, sterilization and disinfection are physical processes, Proper cleaning by water and mechanical action with or without detergents.
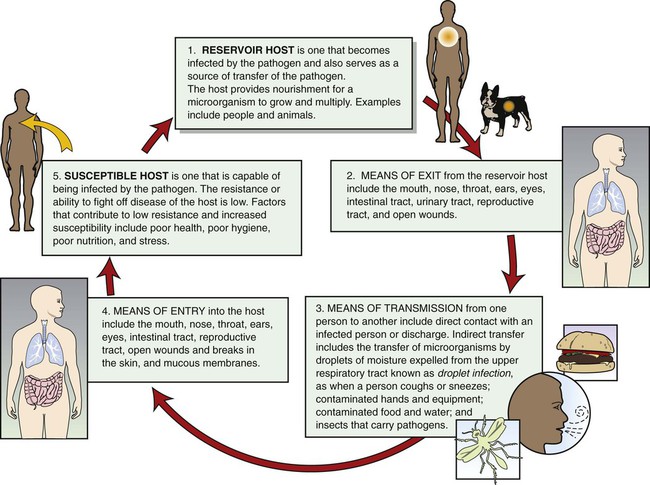

This can be achieve by various methods, Basic medical techniques are focused on breaking the chain of reaction. The nurse follows certain principles and procedures to control and prevent the spread of infection


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
